Family relationships are a very interesting topic, which becomes especially relevant after the wedding ceremony. Who the bride and groom relate to whom after the wedding is an exciting and serious question, especially for newly-made relatives. In the old days, knowing your ancestors and all relatives, blood and non-blood, was considered an honorable and important stage in the beginning of a life together.
In the modern world, young people often do not know the correct names of certain relatives and who is related to whom after the wedding. If a child appears in a family, it is not difficult for him to understand who mom, dad, grandparents, sister or brother are. But with other family relationships, if not confusion arises, then simply elementary ignorance.
How did the relationship arise?
About two hundred years ago, blood relatives traditionally lived together: in the same estate, courtyard or large house. It was also customary, if a son was born in a family, to build him a house next to his parents’, where he could bring his wife after the wedding. It happened that one street in the village consisted only of relatives’ houses. Then the concept of kinship was something common, and everyone knew who was related to whom in the family after the wedding.
In the old days, family relationships, even distant ones, were considered very strong, and mutual assistance and support were not considered a favor. Preserving the family in order to survive and continue it is the main goal of all close people of past centuries, connected in one way or another.
Modern society is far from the old ideas about family. Unfortunately, now even parents and children living close to each other see each other very rarely, not to mention distant relatives. Blood ties are not supported by foundations, free material assistance, or a common family structure, so family relationships, especially distant ones, are under threat and are gradually dying out.
Other relatives of husband and wife
As for other relatives, uncles/aunts, grandmothers/grandfathers, nephews of the wife in relation to the husband or husband to the wife do not have any special names, they are addressed today in the same way as before marriage.
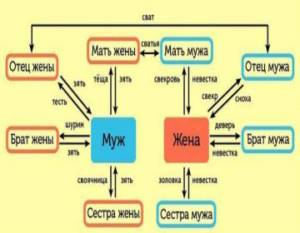
As a general visual aid, we offer you the following table about who belongs to whom and by whom in the family:

The Svadebka.ws portal hopes that you will quickly get used to it and not get confused by the names of your relatives, and reminds you that family ties decide little about who pays for the wedding, because it can be the newlyweds themselves, distant relatives or even friends who have the desire and ability to help in this matter.
Sources:
https://sunmag.me/svadby/kto-komu-i-kem-prihoditsya-posle-svadby.html https://mywed.by/article/nazvaniya-rodstvennikov/ https://svadebka.ws/article/nazvaniya -rodstvennikov/
Relationship by blood
Even if there is no tradition in a young family of knowing all of their relatives, there is still an interest in who is related to whom after the wedding. Family ties, whether strong or not, have a certain degree of importance, especially if they are blood.
The first degree of kinship refers to children and parents, blood sisters and brothers who have a common father and mother. Half-siblings are those who have the same father and different mothers, while half-siblings, on the contrary, have the same mother and different fathers.
The second related degree belongs to grandparents and grandchildren. This level of family relationships is as important as the first, because external similarities, diseases, and other physical and psychological characteristics are passed on from grandparents to the same extent as from parents.
The third degree of relationship is already with the prefix -great: great-grandparents. For grandchildren, these are the parents of their grandparents. This category also includes uncles, aunts, nephews, that is, brothers and sisters of parents.

Relatives from the groom's side
We start, traditionally, with the parents: the groom’s mother is the mother-in-law, the groom’s father is the father-in-law. Of course, not a single girl addresses them like that in person. It is worth saying a few words about the etymology of these related terms: the words “father-in-law” and “mother-in-law” come from the ancient Indian “svacuras” - “blood of all”, that is, this is the recognized head of the clan, whose blood flows in all subsequent generations.
But what to call her husband’s parents after the wedding is determined by each bride herself, in accordance with the traditions of her own family and personal wishes: in some families it is customary to call her husband’s parents “mom” and “dad” as a sign of respect and recognition of their closest people. But in the modern world, the option by first name and patronymic is increasingly taking place - this is no less respectful treatment.
The spouse's brother is the brother-in-law, the groom's sister is the bride's sister-in-law. The groom's cousin for the bride or cousin of a distant family line may have their own names, but it is not worth delving into such a jungle of official names of family ties. If necessary, you can simply use their names. For both the husband’s parents and his brothers and sisters, his chosen one is a daughter-in-law.

Groom's brother - brother-in-law
Groom's relatives
After legal marriage, information about who is related to whom after the wedding acquires special significance. Relatives on the groom's side for the bride will be designated as follows: father - father-in-law, mother - mother-in-law, brother - brother-in-law, sister - sister-in-law, husband's brother's wife - daughter-in-law, and his sister's husband - son-in-law. The parents of the bride and groom call each other matchmakers after the wedding.

Details
Everyone knows the basic related definitions
- mother-in-law and father-in-law, father-in-law and mother-in-law. The most advanced in this matter know who are called matchmakers and godfathers, as well as who a brother-in-law or sister-in-law is. But if we talk about such names as brother-in-law, brother-in-law or yatrovka, then complete confusion in concepts begins. Let's try to figure out who is who by kinship after the wedding.
So, father of the bride. One of the main relatives on the bride's side. However, it must be said that the same person can be called differently depending on family ties:
- for the future husband of the bride - father-in-law,
- for the groom's mom and dad - matchmaker.
The meaning of “matchmaker” is the name of the groom’s parents
and the bride's parents in relation to each other. For example, the groom's father is a matchmaker for the bride's parents, and the mother, accordingly, is a matchmaker.
The mother of the bride for the future husband is called mother-in-law. In modern families, the mother-in-law often takes on the responsibilities of a second mother, since it is the mother-in-law who, most often, helps a young family raise children, as well as prepare delicious dinners and help around the house. Sometimes, in the event of a divorce, the son-in-law maintains friendly relations with the mother-in-law. It should be noted that many different jokes are written about mother-in-law, although, in fact, most conflicts arise between mother-in-law and daughter-in-law.
The bride's sister is a sister-in-law for the groom and his parents. The origin of the word “sister-in-law” is from the adjective “one’s own,” that is, a close person. The brother of the bride for the groom, as well as for the father-in-law and mother-in-law, is the brother-in-law, and the husband of the sister-in-law (sister of the bride) is called the brother-in-law. If the bride's sister has a groom, he is called a future brother-in-law, although he is not considered an official relative. The groom is a son-in-law to his brother-in-law and sister-in-law, just as he is to the bride's parents. It must be said that there is a definition for a son-in-law who lives in his wife’s family; he is called a primak.
Words mother-in-law (mother of the groom)
and father-in-law (father of the groom) are derived from the ancient Indian word “svacuras” “blood of all”, in other words, the respected head of the clan, whose blood flows in subsequent generations.
As for how the daughter-in-law will address her husband’s parents after the wedding, she decides for herself, according to the customs of the family in which she grew up and her own wishes. Many families have a habit of addressing their husband’s parents as “mom” and “dad” as a sign of respect for them. Today, more often, daughters-in-law address their husband's parents by their first and patronymic names, which sounds no less respectful.
For the bride, the husband's brother is the brother-in-law, and the sister is the sister-in-law. The future wife, the parents of the future husband and his brothers and sisters are called daughter-in-law.
In modern society, the names of family ties are becoming less “in demand” and are most often used in provincial outbacks remote from civilization.
The “other halves” (wives) of the brothers are yatras for each other. It is customary to call a brother's wife (regardless of whether it is the bride's brother or the groom) a daughter-in-law.
To perform the baptism ceremony for a child
Godparents are invited. This does not have to be relatives or husband and wife. These people will become godparents for the baby, mom and dad, and in relation to each other they will be called godfather and godfather. Often, families have their own traditions, for example, it is customary to call a grandmother by name, and brothers or sisters by diminutive versions of their names, therefore, when joining a new family, you should ask in advance how best to address one or another of its members.
Special topic: what children from previous marriages are called. The wife’s daughter from a previous marriage, in fact, like the husband’s daughter, is called a stepdaughter, and the husband is a stepfather for the wife’s children born in her first marriage. The son of a husband or wife from a previous marriage is considered a stepson.
It must be said that there are also such concepts: half-blooded (children who do not have a direct blood relationship, when they have the same father and different mothers) or half-uterine (children born from the same mother, but having different fathers) relatives.
If a family consists of numerous relatives, then for a better understanding you can draw up a family tree or a diagram of new relatives and designate all relatives, respectively, with certain names. This will make it easier to remember.
Distant blood relatives
Nowadays, interest in who is related to whom after the wedding has gradually begun to fade away. With the birth of a new family, which will slowly acquire children of its own, distant relatives will not have much importance given the way of modern life. In order to pay tribute to traditions, you need to have a lot of free time, which is limited in the twenty-first century.
If you are interested in finding out who is related to whom after the wedding, you can draw up a family tree, taking into account that its lateral branches also belong to the category of blood relatives. Usually, at the beginning of the family, common ancestors are indicated, which are distant relatives. It is from them that the countdown begins.
The fourth degree of consanguinity represents cousins, grandparents, and great-nephews (grandchildren of siblings).
The fifth degree of relationship is cousins, aunts and uncles, and nephews.
The sixth, most distant, are second cousins, that is, children of cousins of parents.
The remaining degrees of consanguinity are considered very distant and are not tracked by many.

What to call your brother's wife
For clarity, let’s imagine a specific family, otherwise our heads may spin from the endlessly intersecting vectors of kinship. So, there lived two brothers, Ivan and Vasily. Both became serious men and got married. Ivan is on Marya, and Vasily is on Daria. And do you think that we will need to answer the question, for example, from Ivan: “My brother’s wife, who is she to me?” Really, who does he think Daria is now?
The older generation would answer this question that such a woman in Russia was most often called a sister-in-law, in some areas - a zolovaya, and closer to Ukraine she had a different name - bratova or yatrovka.
Each of the young wives - both Marya and Daria - now has a new relative - a daughter-in-law (that is, they are each other's daughters-in-law or intercourse). By the way, not only the father-in-law and mother-in-law can call them daughters-in-law, but also the husband’s brother (that is, Marya became Vasily’s daughter-in-law, and Daria became Ivan’s), and the husband’s entire family.

Relatives not by blood
Very useful and interesting information about who is related to whom after the wedding, if the relationship is not blood. You can read about the close relatives of the bride and groom above, but there are many others who are related by non-blood ties. So, if the groom has a child from another marriage, then for the future wife he will be a stepson or stepdaughter. A wife is considered a stepmother for her husband’s natural son or daughter, and a stepfather is considered a stepfather. The godmother and father (who baptized the child of friends) are godmothers among themselves.
Not blood, but close
There are cases when people who are not related by blood become a family, for example, when a man and a woman get married, having children from previous marriages, or spouses adopt a child. In this case, family members will be called:
- stepmother - stepmother,
- stepfather - stepfather,
- stepson - step-son,
- stepdaughter - stepdaughter,
- named son - adopted,
- named daughter - adopted,
- the named mother and father are the adoptive parents,
- half-brothers and sisters - natural and step-children of each other.
Also, non-relatives but close ones include people whose names these days can be found more often in films and books than in reality:
- milk mother - a woman who breast-fed a step-child in relation to him,
- foster brother or sister - children who are not related to each other, raised by the same woman,
- uncle, mother - a man or woman who looks after and raises a child, today better known as nannies and nannies.

Depth of kind
The clan and its duration depend on the number of generations of children who are related by blood. They are the ones who determine the scale of the family tree. Usually the branches and crown depicted schematically are families of children. Due to the difficulty of tracking weddings, deaths and other events that influenced their family, special chronicles were kept in ancient aristocratic families.
Nowadays, tracking a family lineage deeper than the fourth generation is considered difficult; in this situation, it is especially difficult to understand who is related to whom after the wedding. The relatives of young people (non-blood) often do not have significant significance if there is no close spiritual or friendly connection between these people.
A child born into a family of nephews is called a niece (nephew grandson or granddaughter, great-grandson or great-granddaughter and further down the depth of birth). The grandson of a brother or sister makes a grandparent out of an aunt and uncle, and such children are called great-nephews.

Cousin and its depth
If the bride and groom have cousins, they are also called cousins, then for young children they will also be cousins, but now aunts and uncles. These categories are considered consanguineous, but distant. Knowing your family tree and tracing all branches two or three hundred years ago was considered the privilege of aristocrats and was confirmation of a high position in society. The same applied to simply rich people, landowners and merchants.
In some European countries, the tradition is still preserved to honor their ancestors and draw up a family tree, which is usually traced from father to son. That is why in royal and wealthy families the birth of an heir was of paramount importance for the family.
It is no secret that modern society is far from ideal relationships between relatives, even blood ones. Conflicts based on family troubles, gossip, material and housing problems are increasingly leading to real wars, where there is no place for love and respect for the family. And even the fact of creating a new family, for which it is so important to know who is who after the wedding, the relatives of the groom (or, conversely, the bride) cannot always accept for many reasons.
Who is your brother's wife from the point of view of his sister?
And in the case where two brothers and sisters live in a family, will the brother’s wife be called something different for the sister? No, nothing new has been invented here - for a sister, her brother’s wife will also turn out to be a daughter-in-law or, in other words, a brother’s wife. But this sister herself will already be a sister-in-law for the daughter-in-law. By the way, in some regions they called her “Bindergarden” (probably from an excess of feelings!).
It’s interesting that in the old days cousins were called “bro” or “bro” (that’s where these proud definitions of the 90s era come from!), and their wives, respectively, “bros”. That is, when figuring out: “My brother’s wife - who is she to me?”, know that siblings and cousins, as well as their wives, are defined in slightly different terms.
Nephews
They fall into the category of close blood relationships, and sometimes can even replace children for aunts and children who do not have their own. Nephews are the offspring of half-siblings. They are also first cousins to their aunt and uncle's children.
Unfortunately, it happens that cousins or nephews marry each other. This leads to various genetic pathologies and degeneration. In this case, it is best to know who is related to whom after the wedding. The relatives of the bride and groom establish family relationships that cannot be turned into marriages of people by blood. Meanwhile, in many European and other countries, such marriages are not officially welcomed, but are not prosecuted by law either.

Spiritual kinship
The rite of baptism is important for many families; it is believed that the earlier it is carried out, the better. Therefore, as a rule, a child already has new relatives in the first year of life, and we all know well what the relatives who came to the family in this case are called - godfathers, father and mother; among themselves and in relation to the child’s natural parents, they are considered godfathers and godfather. The godson and goddaughter, respectively, are the girl and boy they baptized. Further, the word godfather (godmother) is added to all relatives on this side. But cross brothers or sisters have a different meaning. This is the name given to people who themselves exchanged crosses. In addition to godparents, there may also be imprisoned parents. This is the name given to those who replace their relatives father and mother at the wedding ceremony.

Grand-relatives
This relationship is more in-depth, and it affects brothers and sisters of different branches of the family tree. For example, when the children of sisters or brothers grow up and start their own families, they start a new branch. Therefore, the more children there are in such marriages, the more magnificent and branchy the crown looks. However, the level of relatedness in all families is determined only by the depth of the roots.
It is possible to decipher the meaning and meaning of the names of all relatives and relatives by blood only by studying the family life of a particular person. In order to understand who a great-nephew is, trace the family relationships of a woman who has a blood brother or sister. For example, her children will be considered nephews for half-blood relatives. Over time, growing up, nephews get married or get married, have their own children, who will already be called grandchildren. In the future, the depth of the clan is determined precisely by nephews, great-grandchildren, and further with the prefix -great-great.
In addition to the well-known names of close relatives and in-laws, there is a huge variety of secondary and tertiary relatives, which can be called habitually or even go beyond the scope of family relations. Modern families increasingly prefer, or this happens for objective reasons, not to track the depth of kinship, and family inheritance is passed on regardless of gender and number of children.
Let’s add a little about relatives, imaginary and real.
And if we assume that Marya, Ivan’s wife, has a married sister, then for Ivan she will be considered a sister-in-law, and her husband, accordingly, a brother-in-law. That is, it turns out that brothers-in-law are family members whose wives are sisters. If we are talking about cousins, then their husbands will be considered cousins-in-law among themselves.
As you can see, by asking the question: “Who is my brother’s wife?”, we slowly figured out the rest of the relationship. And who knows, maybe this information will help you maintain warm relationships in your new family. By the way, a striking example of this is an interesting experiment conducted by British scientists. They gathered previously unknown people into a group, having previously informed some that they were related to each other. It is interesting that in the future it was these people who established the closest friendly relations with each other, assuring the researchers that family feelings suddenly awoke in them.











